 Introduction
Introduction
Swimming is one of the most popular and beneficial activities in the world. It is not only a competitive sport but also a recreational pastime, a survival skill, and a powerful form of exercise that promotes both physical and mental well-being. From Olympic athletes breaking records in pools to families enjoying time at the beach, swimming plays an important role in cultures worldwide.
This article explores the history, techniques, benefits, competitions, and global impact of swimming, and explains why it remains one of the best lifelong activities for health and happiness.
A Brief History of Swimming
Swimming is an ancient practice, with evidence of swimming activities dating back over 7,000 years. Ancient civilizations such as Egypt, Greece, and Rome valued swimming for recreation, military training, and survival.
In modern times, swimming became a recognized competitive sport in the 19th century. The first international swimming competition was organized in London in 1837, and by 1896, swimming was included in the very first modern Olympic Games. Today, swimming is a global sport, with world-class competitions like the Olympics, World Championships, and regional swimming events.
Different Swimming Strokes and Techniques
1. Freestyle (Front Crawl)
-
The fastest and most common stroke in competitive swimming.
-
Emphasizes alternating arm movements and flutter kicks.
2. Backstroke
-
Swum on the back with alternating arm and leg movements.
-
Helps build back and shoulder strength.
3. Breaststroke
-
Characterized by frog-like kicks and simultaneous arm pulls.
-
A slower but highly technical stroke, popular in both leisure and competitions.
4. Butterfly Stroke
-
The most challenging stroke, requiring simultaneous arm movements and dolphin kicks.
-
Builds exceptional strength and stamina.
5. Individual Medley (IM)
-
A race combining all four strokes, testing versatility and endurance.
Benefits of Swimming
1. Physical Health Benefits
-
Full-Body Workout: Engages nearly every muscle group.
-
Cardiovascular Health: Strengthens the heart and lungs.
-
Low-Impact Exercise: Gentle on joints, suitable for all ages.
-
Weight Management: Burns calories effectively, supporting healthy weight.
2. Mental Health Benefits
-
Reduces stress and anxiety through rhythmic breathing.
-
Boosts mood by releasing endorphins.
-
Improves focus, discipline, and confidence.
3. Life Skill and Safety
-
Essential survival skill that reduces the risk of drowning.
-
Equips individuals with water safety knowledge.
4. Accessibility and Inclusivity
-
Suitable for children, adults, seniors, and people with disabilities.
-
Swimming pools and open water make it accessible worldwide.
Competitive Swimming and Major Events
Competitive swimming is a thrilling sport featured in international competitions, including:
-
Olympic Games: Swimming has been a core Olympic sport since 1896.
-
FINA World Championships: Hosts the best swimmers globally.
-
Regional Games: Events like the Commonwealth Games and Asian Games highlight global talent.
-
College and School Competitions: Inspire youth participation and future champions.
Apart from professional swimming, recreational and fitness swimming remains popular in gyms, schools, and local clubs.
Swimming for All Ages
Children
-
Builds motor skills, discipline, and water confidence.
-
Encourages healthy growth and fitness habits early.
Adults
-
Provides stress relief and helps maintain fitness.
-
Works as a low-impact alternative to running or gym workouts.
Seniors
-
Supports mobility and reduces joint pain.
-
Improves flexibility and heart health in a safe environment.
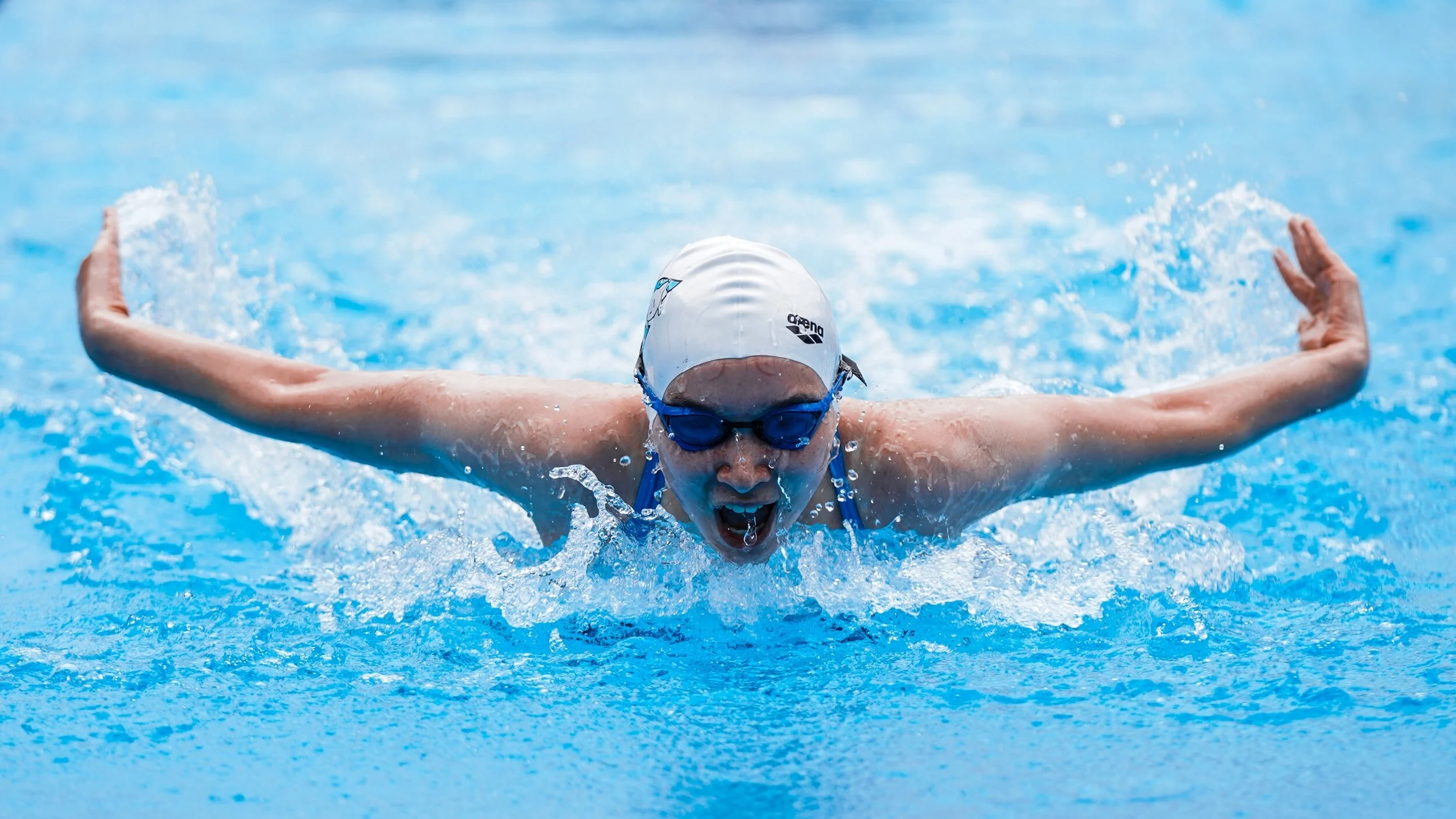 Challenges in Swimming
Challenges in Swimming
-
Accessibility: Limited pools or water facilities in some regions.
-
Safety Concerns: Risk of drowning without proper training or supervision.
-
Cost Factor: Professional training and competitive swimming can be expensive.
-
Environmental Impact: Concerns about water pollution in open-water swimming.
Swimming and Global Popularity
Swimming is popular in nearly every country, with strong followings in the USA, Australia, China, Japan, and Europe. Iconic swimmers like Michael Phelps, Katie Ledecky, Ian Thorpe, and Mark Spitz have elevated the sport’s visibility worldwide.
Additionally, swimming is encouraged as part of fitness programs, school curriculums, and medical rehabilitation plans, making it both a sport and a universal life skill.
The Future of Swimming
The future of swimming looks promising, shaped by technology, inclusivity, and sustainability:
-
Technology: Underwater cameras, stroke analysis, and smart swimwear help athletes improve performance.
-
Inclusivity: Adaptive swimming programs are making the sport accessible to people with disabilities.
-
Sustainability: Eco-friendly pool systems and awareness about ocean protection are growing.
-
Global Growth: Expansion of swimming academies and school programs in developing nations.
Conclusion
Swimming is far more than a sport—it is a pathway to health, confidence, and joy. Whether pursued competitively or as a recreational hobby, swimming offers unmatched benefits for the body and mind. From ancient traditions to Olympic glory, swimming has stood the test of time as one of humanity’s most cherished activities.
As people worldwide continue to dive into pools, lakes, and oceans, swimming will remain a lifelong skill and global sport that promotes health, safety, and community.


You must be logged in to post a comment.